- Bone Health
- Immunology
- Hematology
- Respiratory
- Dermatology
- Diabetes
- Gastroenterology
- Neurology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Rare Disease
- Rheumatology
Contributor: No Animal Testing of Biosimilars—US Congress Begins Amendment to BPCIA
Sarfaraz K. Niazi, PhD, a professor and biosimilar advocate, chronicles the current efforts to remove animal testing from application requirements for biosimilars under the Biologics Price Competition and Innovation Act (BPCIA), including recent congressional action.
Sarfaraz K. Niazi

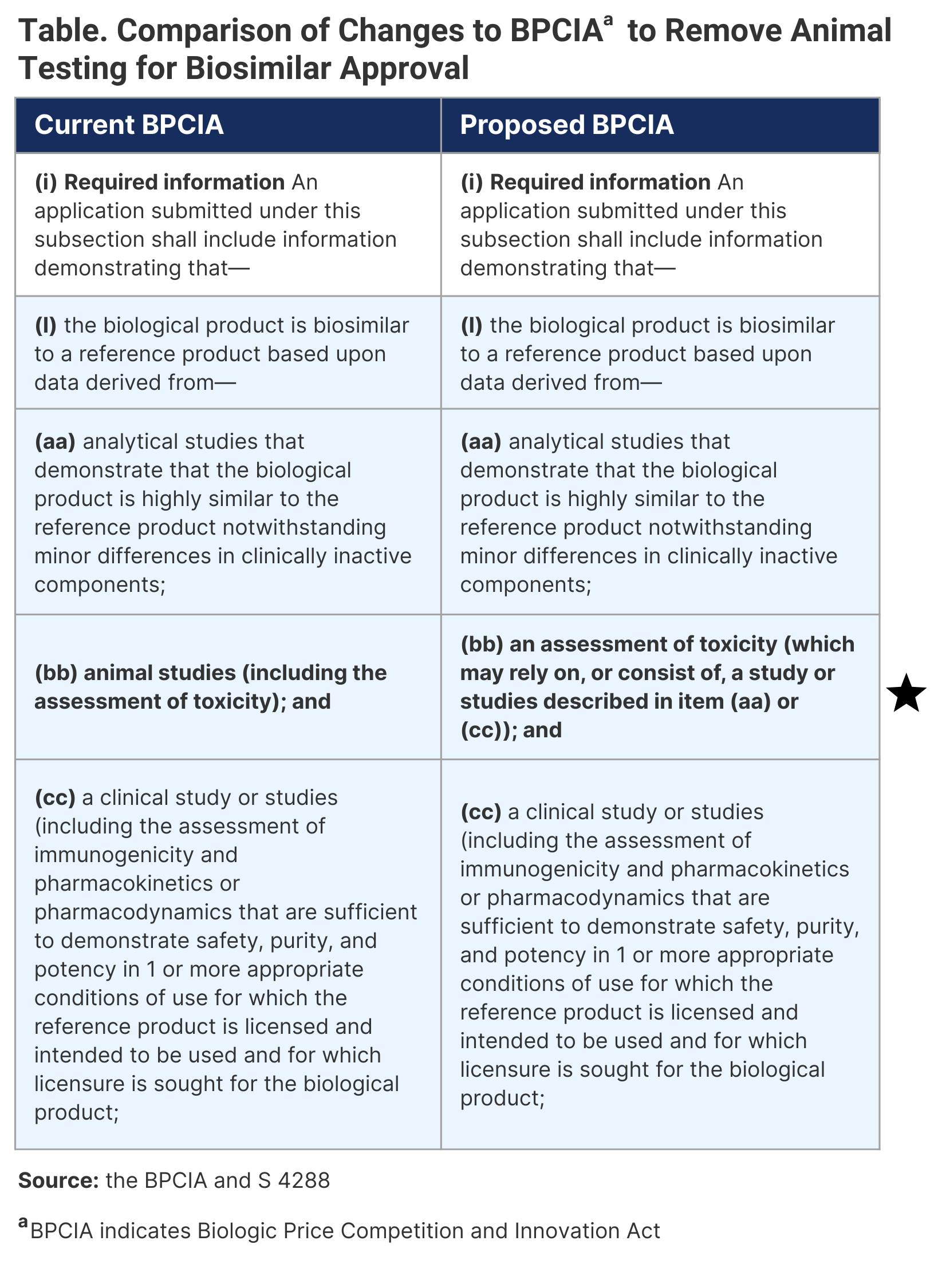
It is now well established that animal testing of biosimilars is unnecessary. I was able to provide much evidence and logic to convince the US FDA and the US Congress to amend the Biologics Price Competition and Innovation Act (BPCIA) to remove animal testing.1 After months of discussions, I am pleased to inform that Senator Ben Ray Luján (D-New Mexico) has admitted an amendment to BPCIA (S 4288) that will remove the mention of animal studies as shown in Table.2
The FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research has long encouraged exploring the use of NAMs, also known as new approach methodologies, to improve regulatory efficiency and potentially expedite drug development of new biotechnology-derived products:
Click to enlarge.
“A weight-of-evidence approach is practiced for biotechnology-derived products when a carcinogenicity assessment is warranted. Genotoxicity [damage to DNA or chromosomes] testing is generally inappropriate for biological products and is not part of the assessment. When sufficient information is available, the need to conduct additional nonclinical studies, regardless of whether the biologic is active and testable in a rodent bioassay, is not warranted. If the assessment does not suggest carcinogenic potential, a rodent bioassay is considered unlikely to add value, and no additional nonclinical testing of biologic products is recommended. Prior knowledge of target-based risks figures prominently in developing a strategy to assess the carcinogenic risk of each new biologic because the nonspecific activity of such molecules is generally considered to be low.” 3
It should have been obvious that if data from animal testing is of little value in the development of new biological drugs, then it should be of a lesser value for products that have already been approved. However, the mention of "animal studies" in the BPCIA had stirred up animal toxicology and pharmacology testing and taking them overboard, resulting in the FDA rejecting to review these data (number rejected/number submitted; Inflectra, infliximab, n = 2/4; Cyltezo, adalimumab, n = 2/6; Mvasi, bevacizumab, n = 2/7; Retacrit, epoetin alfa, n = 13/15; and Ziextenzo, pegfilgrastim, n = 8/13). In reality, there should have been no animal toxicology testing.
There are enough votes in the Senate to pass this bill. This would have a significant impact on the approval guidelines of biosimilars. I am confident that the European Medicines Agency (EMA) will also come up with a definitive statement, even though this is an assumed status with the EMA. The biggest impact will be felt across the globe among the regulatory agencies that follow the World Health Organization guidelines that continue to insist extensive animal testing.4
My next target is to remove interchangeability as well as clinical efficacy testing of biosimilars; but for now, I am ready to accept this change to bring more rationality to the development of biosimilars. There would be a significant reduction in the testing time and cost—both relevant to making biosimilars affordable. In addition, animal suffering would be reduced.
Author Bio
Sarfaraz K. Niazi, PhD, is an adjunct professor of biopharmaceutical Sciences at the College of Pharmacy at the University of Illinois at Chicago and a patent law practitioner. Additionally, he is the founder and executive chariman at Pharmaceutical Scientist, Inc, the executive chairman of Karyo Biologics, and the founder of Adello Biologics, which was acquired by Kashiv Biosciences in 2019. Niazi also serves on the advisory board for The Center for Biosimilars®.
References
- Niazi SK. The coming of age of biosimilars: a personal perspective. Biologics. April 20, 2022;2(2):107-127. doi:10.3390/biologics2020009
- Luján Introduces Legislation to Reduce Animal Testing. Press release. Senator Ben Ray Luján; May 20, 2022. Accessed June 27, 2022. https://www.lujan.senate.gov/newsroom/press-releases/lujan-introduces-legislation-to-reduce-animal-testing/
- Avila AM, Bebenek I, Bonzo JA, et al. An FDA/CDER perspective on nonclinical testing strategies: classical toxicology approaches and new approach methodologies (NAMs). Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 2020;114(2020):104662. doi:10.1016/j.yrtph.2020.104662
- Van Norman GA. Limitations of animal studies for predicting toxicity in clinical trials: Is it time to rethink our current approach? J Am Coll Cardiol Basic Trans Science. November 2019;4(7):845-854. doi:10.1016/j.jacbts.2019.10.008.
Newsletter
Where clinical, regulatory, and economic perspectives converge—sign up for Center for Biosimilars® emails to get expert insights on emerging treatment paradigms, biosimilar policy, and real-world outcomes that shape patient care.
