- Bone Health
- Immunology
- Hematology
- Respiratory
- Dermatology
- Diabetes
- Gastroenterology
- Neurology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Rare Disease
- Rheumatology
Roundup: Adalimumab Biosimilar Advancements and a Biosimilar Pill
Alvotech gains an EU marketing recommendation for AVT02, a proposed adalimumab biosimilar; New Zealand may give preferential status to Amgen's adalimumab biosimilar; BioFactura looks to deliver ustekinumab via a robotic pill.
Alvotech of Reykjavik said it has received a recommendation for approval of its adalimumab biosimilar (AVT02) from the Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) of the European Medicines Agency.
The approval concerns a high-concentration, citrate-free 100-mg/mL formulation of adalimumab, referencing Humira. The positive opinion from the CHMP will go to the European Commission, which is the authority that has the power to authorize marketing of the drug in the European Union and EU member states (Iceland, Liechtenstein, and Norway).
Adalimumab inhibits the activity of tumor necrosis factor, a protein in the body that causes inflammation. The drug is used in the treatment of multiple conditions, including Crohn disease, rheumatoid arthritis, and psoriatic arthritis.
Alvotech noted that Humira has annual sales of about $20 billion. AbbVie, the owner of the Humira franchise, has captured significant market share with its own high-concentration, citrate-free formulation, and Alvotech’s product has the potential to take a portion of that business away from the drug company giant.
However, Alvotech would not be the first company to bring a high-concentration biosimilar of adalimumab to market in the European Union. Celltrion Healthcare achieved that milestone in February 2021 when it received European Commission approval to market Yuflyma, a 100-mg formulation.
Both Celltrion and Alvotech hope to gain FDA approval to market their high-concentration adalimumab biosimilars in the United States.
Biosimilar Adalimumab in New Zealand
New Zealand’s Pharmaceutical Management Agency (Pharmac), the government entity that decides which medicines are subsidized for use in hospitals and community settings, said it is contemplating making the adalimumab biosimilar Amgevita the principal adalimumab product in that country, displacing Humira, in February 2022.
Pharmac said the proposed change would save money. “The list price of Amgevita would be lower than the current adalimumab list price,” Pharmac said.
Amgevita is available in citrate-free formulation, which reduces pain on injection, and is dispensed in prefilled pens and syringes in doses of 20 mg/0.4 mL and 40 mg/0.8 mL; however, Pharmac said dosing restrictions would be removed for patients using Amgevita.
Higher concentration Humira is available, also in citrate-free formulations, and it was not explained whether the removal of dosing restrictions on Amgevita is intended to compensate for that. A public comment period on the proposal closes on September 22, 2021.
Patients who start on adalimumab treatment would automatically receive Amgevita, and those who are currently treated with Humira would have to switch to Amgevita by September 1, 2022. The Amgevita preference would continue at least through June 2026.
“This proposal results from a competitive process for the principal supply of funded adalimumab. It would release significant funds for Pharmac to invest in other medicines for the benefit of New Zealanders,” the government organization said.
“There’s a (Biosimilar) Pill for That”
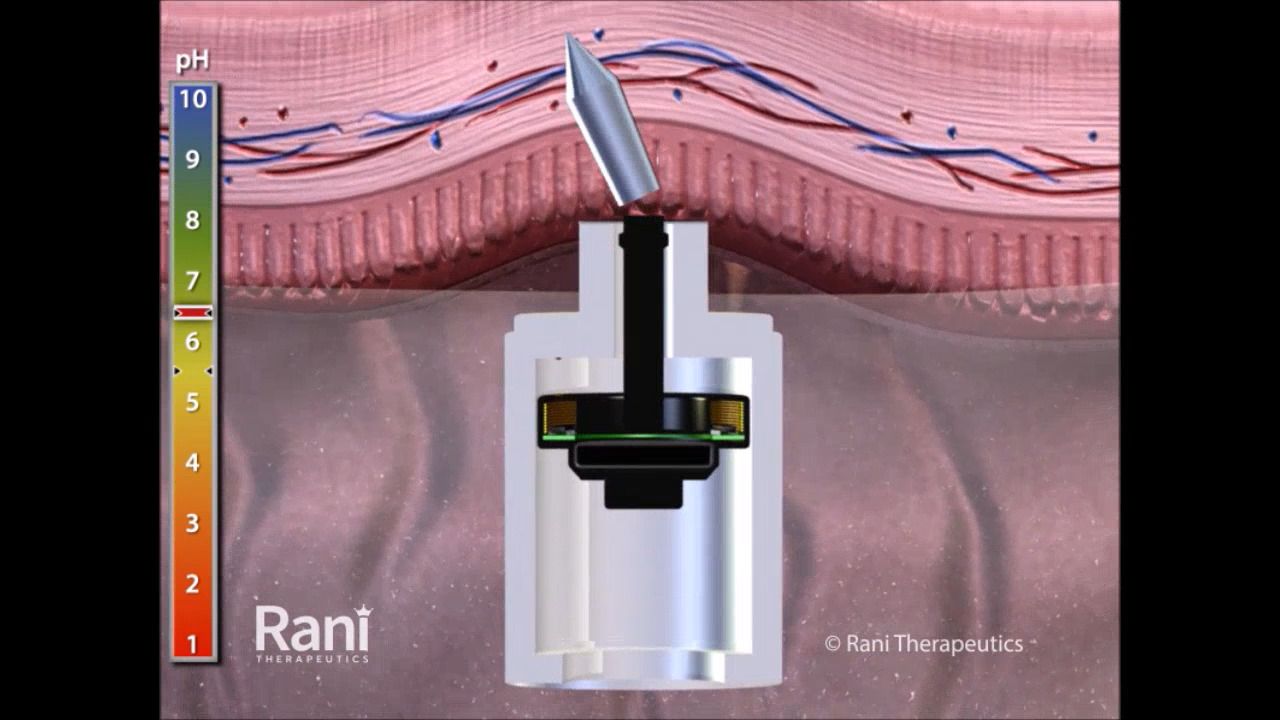
BioFactura, a Maryland-based biopharmaceutical company, said it will partner with Rani Therapeutics to package its proposed ustekinumab biosimilar (BFI-751) in the form of a robotic pill that is ingested and delivers a drug payload into the small intestine via injection.
The ustekinumab biosimilar candidate would reference Stelara and be used in the treatment of Crohn disease, ulcerative colitis, plaque psoriasis, and psoriatic arthritis. Ustekinumab reduces inflammation that causes these conditions.
The robotic pill concept, if successful, would substitute for subcutaneous or intravenous administration, BioFactura said. “The RaniPill capsule is designed to be a pain-free alternative for delivering large molecule chronic disease treatments that are typically administered via injection,” the company said.
Rani Therapeutics will conduct preclinical studies to determine whether pill administration is suitable for ustekinumab administration.
BioFactura Australia, the BioFactura subsidiary charged with development of BFI-751, initiated a phase 1 double-blind trial in April 2021 to compare pharmacokinetics, safety, and tolerability between the originator and biosimilar candidate agents.
Rani Therapeutics created a simulation video that demonstrates how the robotic pill would travel through the body to deliver a drug agent.
For Related Reading:
The Center for Biosimilars® recently interviewed Anil Okay, chief commercial officer for Alvotech, about the company's biosimilar development and marketing plans. Okay explained why the company believes the high concentration formulation, AVT02, will have a marketing advantage.
Newsletter
Where clinical, regulatory, and economic perspectives converge—sign up for Center for Biosimilars® emails to get expert insights on emerging treatment paradigms, biosimilar policy, and real-world outcomes that shape patient care.